As a sportsman, by now you should know that the body gets amino acids from food, which it uses to build every tissue in the body including the muscles. You should also know that every amino acid is different from the other. There are three most essential amino acids, which are necessary for the building of tissues; they are leucine, isoleucine and valine. For this reason, they are the most famous and the most vital amino acid supplements.
Considering what they do for the body daily, these amino acids are not just BCAAs, they are AAAs: amazing Amino Acids. These amino acids are also essential for boosting energy, causing delay in the breakdown of muscle and boosting your body's fat burning capabilities. Another essential function of the BCAAs is aiding in muscle reconstruction and repair. In a nutshell, BCAAs are used to build the body. This article will help guide you with the knowledge you require about branched-chain amino acids.
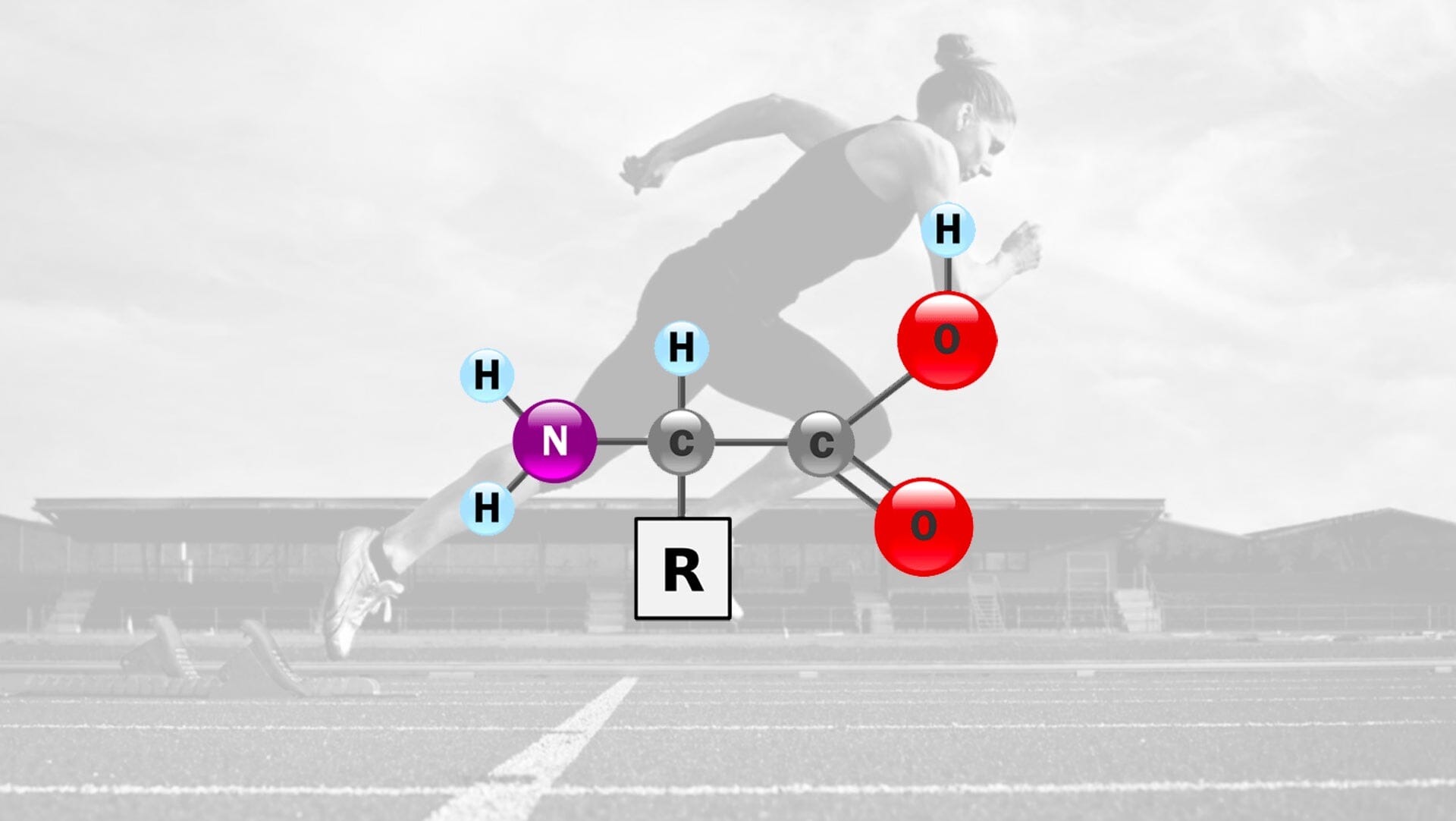
Amino acid synthesisGenerally, amino acids make up proteins, which are essential for building muscles. They help you get the best from your muscles during training and exercising. As a result, when taking your supplements, they should make the foundation. There are two ways of classifying amino acids; essential and non essential.
Essential simply means you must acquire them through food while non essential are those that the body can produce. There are at least 20 known amino acids including the commonly known arginine, glutamine and tryptophan. But the branched-chain amino acids(BCAAs); aminos leucine, isoleucine and valine are the ones that stand out.
Amino acids, especially BCAAs, are well known among athletes due to their ability to improve muscle size directly. Muscles are built using proteins and proteins have amino acids in structures that can resemble a pearl necklace, or a chain. Muscles grow through a process called protein synthesis where amino acids are connected together, forming protein chains, which in turn form muscle and other tissues in the body.
When you take in amino acids through food, they are broken down in the intestines and are taken straight to the liver. The liver decides what to do with them before they are transported to the whole body and used for tissue repair. Most amino acids are broken down by the liver for fuel, but the tree branch-chained amino acids are transferred to the other parts of the body to build tissues.
The roles of branch-chained amino acids Leucine: Ignites muscle growthLeucine is likened to what a key is to an ignition when it comes to the body. If the muscle cell or muscle fiber is the car, then the Leucine is the key that turns it on. It simply starts the process of muscle protein synthesis. Scientifically, Leucine is responsible for the turning on the mTOR that lights up the whole process.
Taking supplements rich in Leucine during training leads to at least 30 percent muscle protein synthesis enhancement. Research has also shown that athletes who take their Leucine supplements with their post workout meals show better muscle protein synthesis compared to those who only take normal meals.
The other importance of Leucine is to improve insulin levels. It promotes the release of insulin from the pancreas, which improves the intake of amino acids by the cells.
Valine: the energizerA number of studies have made it clear that supplements with BCAAs taken before exercise improve the muscle energy and reduce fatigue since the amino acid that is ingested is used as a source of energy. This comes in handy during heavy exercising such as weight training.
During exercise, the brain takes up a huge amount of tryptophan, which is the amino acid that leads to drowsiness and fatigue after a heavy meal once it is converted to serotonin. The more the brain takes in tryptophan the more the brain causes fatigue and lack of endurance on the muscles. Valine is known to compete with tryptophan for entry into the brain, reducing the intake of tryptophan, which reduces fatigue.
Isoleucine: not the leastThis amino acid is essential mainly for fat burning in a way that is different from what leucine does. It stimulates special receptors in the cells that cause fat oxidation genes to work better leading to higher rates of fat burning.
Essentially, amino acids are for developing muscles, both in building up and repairing them. There are three amino acids that are treated specially by the body; they are Leucine, valine and Isoleucine. These are the best for muscle growth and burning of fats.


![Palmitoylethanolamide (PEA) Supplement Guide: Benefits, Dosage & Complete Science Review [2026]](http://qisupplements.com/cdn/shop/articles/Yolk-Eggs_28998241-4462-4b45-8d53-8ef5c31f18d4.jpg?v=1770944354&width=1080)

